IDENTITY - SysFEAT Foundation Ontology Map
| Description | Top level map of SysFEAT patterns. It is layered in three levels:: 1. The basic fondations of modeling constructs describing concepts, their relationships and their classification: the Upper Ontology. 2. The shared characteristics of Asset Blocks: the Architecture Assets. 3. The structure and behaviors of systems in their environment: the Systemic Operating Ontology. The map also includes two dimensions required to ensure enterprise management: 1. Transformation initiatives: the Initiative and Transformation Pattern. 2. Gouvernance activities and instruments: the Governance Pattern. |
|---|---|
| Dictionary |  SysFEAT Upper Ontology
SysFEAT Upper Ontology |
DIAGRAM
DOMAINS
| Domain | Description |
|---|---|
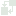 Architecture Packaging
Architecture Packaging |
|
 Governance Pattern
Governance Pattern |
The Governance Pattern domain defines organizations and instrurments required to govern Enduring Initiatives. |
 Initiative and Transformation Pattern
Initiative and Transformation Pattern |
The Initiative and Transformation Pattern domain defines management concepts required for transformation initiatives. It provides principles for the coordination of large scale initiatives evolving over time ( Enduring Initiative and their Initiative Stages). |
 Model Block Packaging
Model Block Packaging |
The Model Block Packaging family of concepts defines the different kind of Building Blocks used in system and enterprise modeling: . Model Building Blocks. . Annotation Blocks . Model Property Blocks. |
 Systemic Operating Ontology
Systemic Operating Ontology |
The Systemic Operating Ontology domain bundles sub-domains used to model how a system, including an enterprise, operates/functions in its environment. It includes Agents, Action Processes, interactions , Behavioral Rules, Capabilityies, Outcome Events, Information Assets and Directives. |
 Upper Ontology
Upper Ontology |
The Upper Ontology domain encompasses five fundamental domains that establish the foundation for the modeling syntax and semantic. 1) The Elementary Graph defines basic constructs for relating and classifying elements in a directed graph. 2) The Reflexive Knowledge Graph defines the elementary constructs of Entity, Relationship and their multi-level classification. Its provides the foundation for open meta-modeling. 3) Packaging, as aspect of modularity, defines syntactic constructs used to group reusable entities (Building Blocks) into modules called Containers. 4) Compositionality, another aspect of modularity, defines the syntactic constructs used to build Entitys that have an internal structure and boundaries. 5) The 4D Composite Knowledge Graph defines Bounded Individuals (entities that exists over space and time) how they are composed (mereology), qualified (properties) and connected, enabling effective representation of meaning. |